ON THIS PAGE
SmartSpace.ai Workflows & Use Case Setup
Workflows – Understanding JSON Configuration
Understanding JSON Configuration
Overview
The JSON configuration in SmartSpace is the underlying structure that defines how flows are constructed and executed. Each flow is represented as a JSON object, which outlines the inputs, outputs, blocks, and connections that make up the flow. Understanding this configuration is crucial for advanced users who want to customize or troubleshoot their workflows at a deeper level.
Structure of the JSON Configuration
A typical JSON configuration in SmartSpace consists of the following key elements:
Inputs: The inputs section defines the data that enters the flow. Each input is described by a name and a JSON schema, which specifies the expected data structure.
Example:

Outputs: The outputs section defines the data that the flow produces. Like inputs, each output is described by a name and a JSON schema, which outlines the structure of the output data.
Example:

Blocks: The blocks section is where the core functionality of the flow is defined. Each block represents a specific operation or action within the flow and includes details such as the block type, configuration settings, and any tools or sub-blocks it may use.
Example:

Connections: The connections section defines how data flows between the different blocks. Connections link the output of one block to the input of another, ensuring that the data moves correctly through the workflow.
Example:

Customizing Flows with JSON
While the Workflow Designer provides a visual interface for building and modifying flows, advanced users can edit the JSON configuration directly to fine-tune their workflows. Here are some ways you can customize flows using JSON:
Modifying Block Configurations: Adjust settings within individual blocks to change their behavior. For example, you can tweak the “llm_config” in an LLM block to alter the model or parameters used.
Adding New Blocks: You can add new blocks to a flow by defining them in the blocks section and then creating the necessary connections in the connections section.
Customizing Inputs and Outputs: You can redefine the structure of inputs and outputs to better match the data your flow needs to handle. This might involve changing the JSON schema definitions or adding new input/output fields.
Editing and Validating JSON Configuration
You can edit the JSON directly by clicking on the green checkbox icon. This will open a text block to change the JSON directly. You can edit at different sub-levels so you may need to click on a parent level to access the part of the JSON definition you need to edit or if you want to add additional items to an array property.
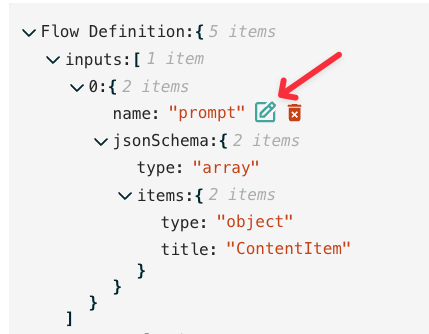
The JSON is validated automatically and will not save unless it is valid. Don’t get caught out by a hanging comma!
Copy Flow Definitions Between Workspaces
The beauty of the JSON definition lies in the ability to quickly copy a definition from one workspace and paste it into another to load in that workflow. Simply edit the top-level block, copy-all, go to the new workspace, edit the top block, paste in the copied definition and save the definition. You will immediately see the visual editor updated with the new workflow. From there you can make any configuration adjustments as needed.
Best Practices for JSON Configuration
Keep Backups: Before making significant changes to your JSON configuration, save a backup of the original configuration.
Document Changes: Maintain clear documentation of any modifications you make to the JSON, including the rationale and expected outcomes.
